No products in the cart.
Return To ShopWe ship globally.
We have special channel shipping
on many brands for guaranteed delivery.
Ask us on [email protected]
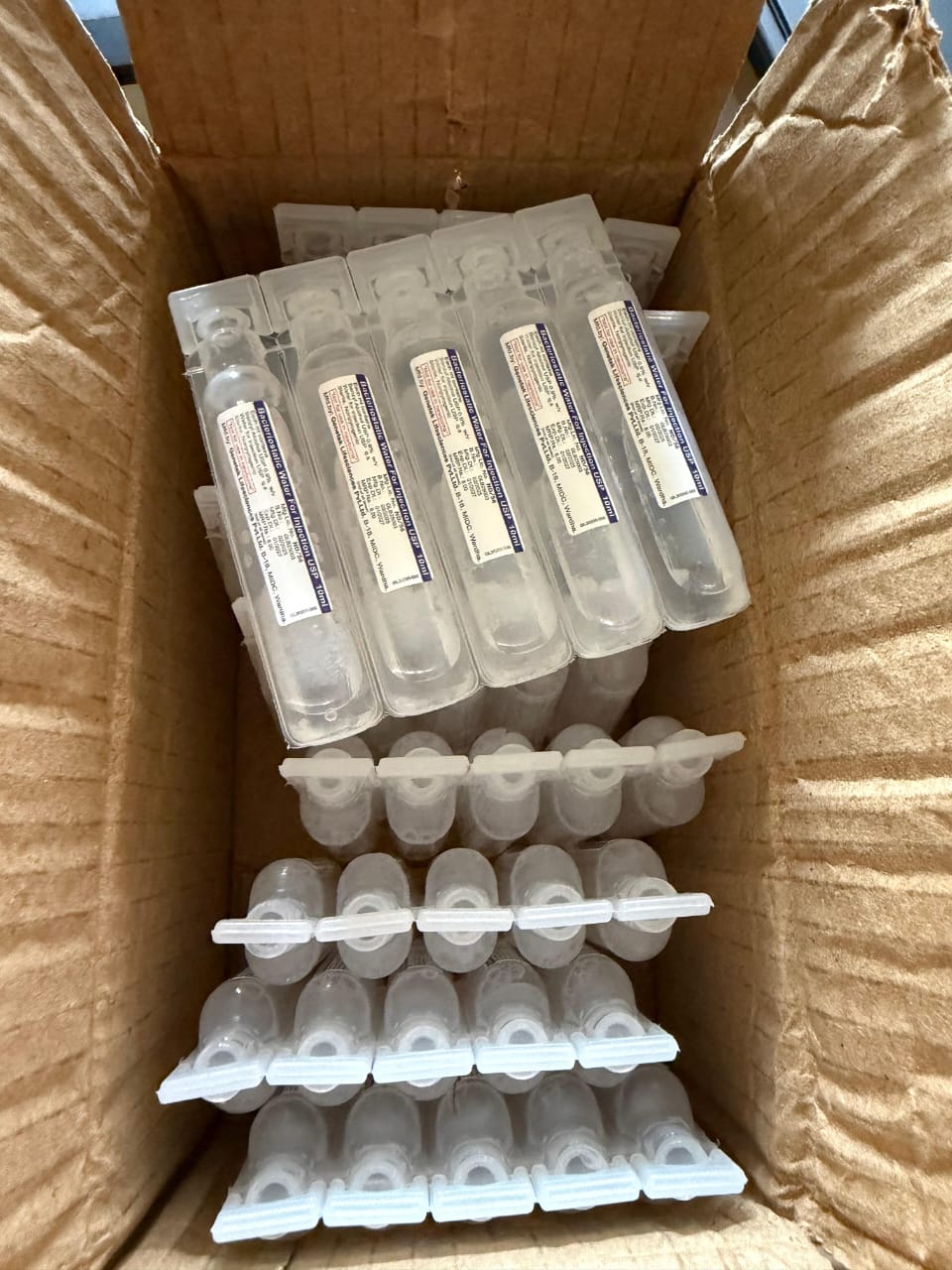
Bacteriostatic water is a sterile, nonpyrogenic preparation of water for injection that contains a bacteriostatic preservative, typically 0.9% benzyl alcohol. This preservative is an agent that inhibits (prevents) the growth of bacteria in the solution.
It is used almost exclusively in medicine as a diluent or solvent for preparing injectable medications, particularly those supplied in multi-dose vials.
How Bacteriostatic Water is Used
The primary function of bacteriostatic water is to safely prepare medications for injection (parenteral use) that require multiple withdrawals from the same vial over a period of time.
- Diluting/Reconstituting Injectable Drugs: Many medications, especially those that come in a freeze-dried powder (lyophilized) or concentrated liquid form, must be mixed with a sterile liquid before they can be administered via injection. Bacteriostatic water is added to dissolve or dilute the drug to its proper, safe concentration.
- Supporting Multi-Dose Vials: Because it contains the bacteriostatic agent, it allows for repeated withdrawals from the same vial (multi-dose container) without the solution becoming contaminated with bacteria. Once opened, vials reconstituted with bacteriostatic water are typically safe to use for up to 28 days (or as specified by the drug manufacturer). This provides convenience and reduces waste for patients who need regular injections at home (e.g., certain hormone therapies or vitamin injections).Injection Routes: The resulting solution (drug mixed with bacteriostatic water) can then be administered via:
- Intravenous (IV)
- Intramuscular (IM)
- Subcutaneous (SC)
Important Considerations
- NOT a Drug Alone: Bacteriostatic water is a solvent or diluent, not a medication itself. It should never be injected directly into the body without being mixed with a drug. Injecting it alone (as it is not isotonic) can cause the breakdown of red blood cells (hemolysis).
- Not for Neonates: Due to the potential toxicity of the preservative benzyl alcohol, bacteriostatic water should not be used for preparing medications for newborns (neonates). Only preservative-free sterile water for injection is recommended for this age group.
- Sterile Water Difference: Sterile water for injection does not contain a preservative, so it is generally intended for single-use only to prevent microbial contamination after the vial is punctured. Bacteriostatic water, with its preservative, is the option that enables multiple uses.